Table of contents
- This episode: Amazon Simple Email Service. In this Hello, Cloud blog series, we're covering the basics of AWS cloud services for newcomers who are .NET developers. If you love C# but are new to AWS, or to this particular service, this should give you a jumpstart.
- Amazon SES : What is it, and why use It?
- Our Hello, SES Project
- Where to Go From Here
- Further Reading
This episode: Amazon Simple Email Service. In this Hello, Cloud blog series, we're covering the basics of AWS cloud services for newcomers who are .NET developers. If you love C# but are new to AWS, or to this particular service, this should give you a jumpstart.
In this post we'll introduce Amazon SES and use it to send mail from a .NET program. We'll do this step-by-step, making no assumptions other than familiarity with C# and Visual Studio. We're using Visual Studio 2022 and .NET 6.
Amazon SES : What is it, and why use It?
"I do love email. Wherever possible I try to communicate asynchronously." —Elon Musk
Amazon Simple Email Service (hereafter "SES") is a service for sending and receiving email messages. AWS describes it as "a cost-effective, flexible, and scalable email service that enables developers to send mail from within any application". You can use SES for transaction emails (such as order confirmations), marketing emails (such as a newsletter), or bulk email (such as notifications).
You can send email with SES via the AWS console or with the AWS CLI. Programmatically, you can send mail using Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) or the AWS SDK. Sending mail works like this:
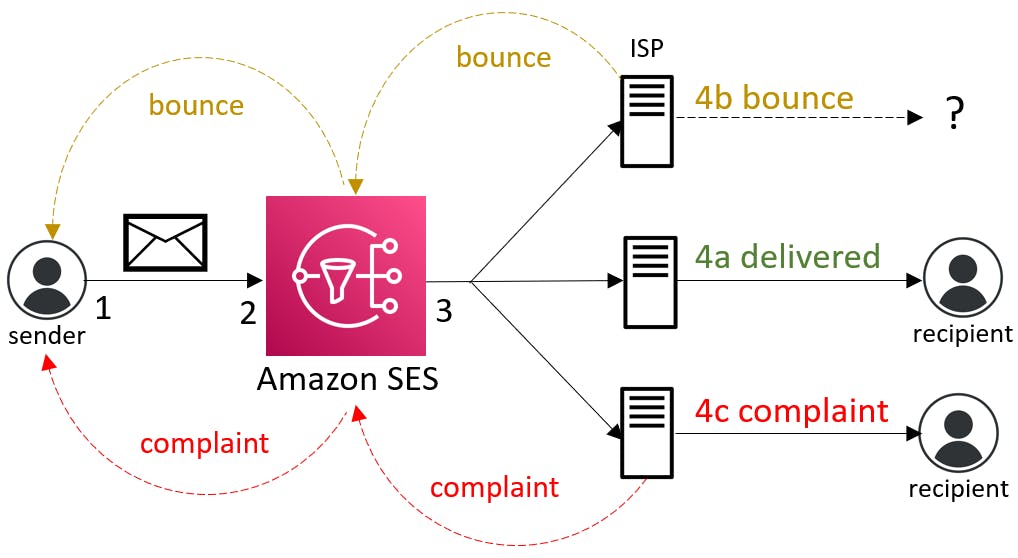
A client application uses the Amazon SES to request sending mail to one or more recipients.
If the request is valid, Amazon SES accepts the email for delivery.
SES sends the message to the recipient's receiver ISP.
Several things can happen at this point:
a. The ISP delivers the message message to the recipient's inbox.
b. A bounce notification is sent because the recipient's email address does not exist. SES forwards the notification to you, the sender.
c. The message is received but is considered to be spam, and a complaint is made with the ISP. The complaint is forwarded to you the sender by SES.
While sending email is a dominant activity with email services, you can optionally receive email as well with SES. You can accept or reject mail based on criteria such as email address.
As email abuse is rampant, a top concern for email senders is sender reputation. SES has features for managing IP reputation, including a mailbox simulator you can use for testing without impacting your sender reputation. SES provides 3 deployment options:
| Deployment Option | Description | Notes |
| Shared IP Addresses (default) | IP addresses shared with other SES customers. | Reputations carefully monitored |
| Dedicated IP Addresses | Lease dedicated IP addresses | Manage your own IP reputation |
| Owner IP Addresses | Use IP addresses you already own (BYOIP) | Leverage current investments |
Features of SES include simple integration, efficient mail delivery, bounce and complaint notifications, and performance analysis.
The AWS Free Tier allows you to send 62,000 messages per month at no charge from an application hosted in Amazon EC2 or AWS Lambda. However, you are responsible for some fees such as EC2 data transfer fees, so read over the details.
Our Hello, SES Project
We will write a .NET console program that sends mail via SES, using the Amazon SDK for .NET.
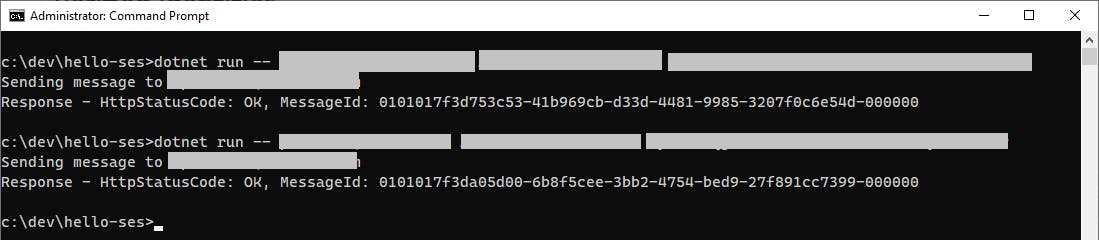
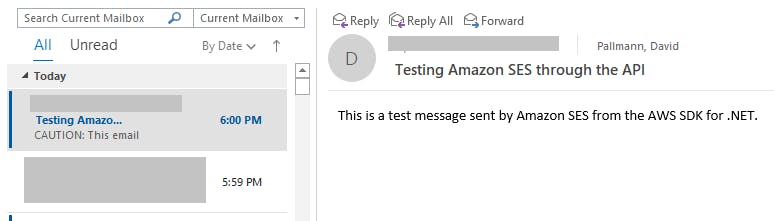
One-time Setup
For any of the tutorials in the Hello, Cloud series you need the following:
- An AWS account, and an understanding of what is included in the AWS Free Tier.
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2022. If you're using an older version of Visual Studio you won't be able to use .NET 6. If you use a different IDE, you may have to find alternatives to some tutorial steps.
- AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio. You'll need to configure the toolkit to access your AWS account and create an IAM user. Your default AWS profile will be linked to this user when running programs from the command line.
Step 1: Work with Amazon SES in the AWS Console
In this step, you'll configure an Amazon SES identity that you can use for programmatically sending email.
Sign in to the AWS console and select the region you want to work in at top right. We're using Oregon.
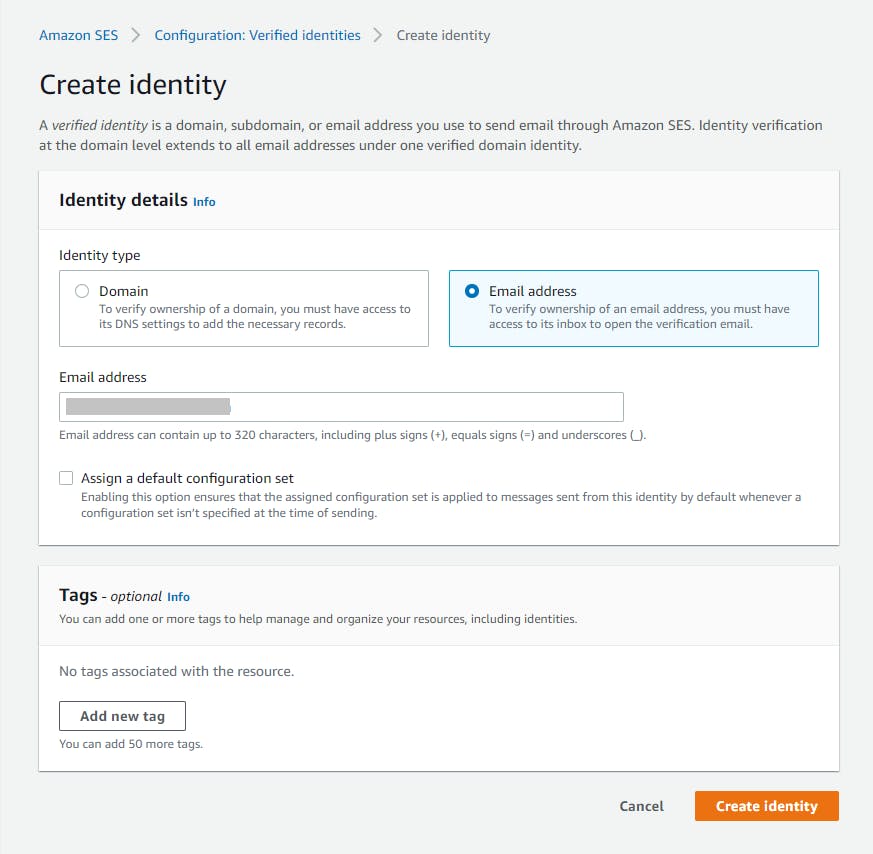
Find the Send your first email panel at right and click the Create identity button.
On the Create identity page, enter/select the following:
a. Identity type: select Email address.
b. Email address: enter an email address you own that you want to use for testing.
c. Click Create identity.
Go to your email inbox where an email from Amazon Web Services should be waiting.
Review the mail and click the link to verify. You see a confirmation message.
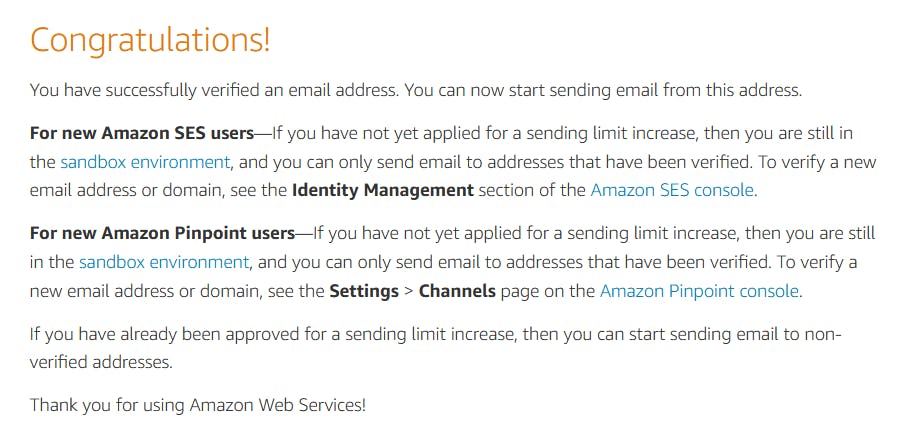
Note the message content: at present you are in a sandbox with Simple Mail Service until you request a sending limit increase. That means you will only be able to send mail to verified email addresses. At the moment, you can only send mail to your own email account.
Refresh the AWS console page, which should now show Identity status Verified.
Add some additional email addresses of yours or people you know who are willing to help you test. On the left panel, click Verified identities. For each identity you wish to add:
a. Click Create identity.
b. Select Email address.
c. Enter the email address.
d. Click Create identity.
e. Ask the email address owner to respond to the Amazon Web Services email and verify their email address.
Now you have several email addresses you'll be able to send mail to, even while in sandbox mode.
Step 2: Obtain Access Keys
In order to use SES from code, you will need access keys.
In the AWS console, navigate to Identity and Access Management (IAM). You can enter iam in the search bar.
Select Users from the left panel.
Click your AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio user to view its details.
Select the Security credentials tab.
In the Access key section, click Create access key to create an access key. Download the CSV with the access key and secret key. Record that information in a secure place, then delete the CSV file.
Step 3: Create a .NET Program for Sending Email
In this step, you'll write a .NET program that can send email via SES.
Open a command/terminal window and CD to a development folder.
Enter the dotnet new command below to create a .NET console program.
dotnet new console --name hello-ses
Launch Visual Studio and open the hello-ses project.
In Solution Explorer, right-click the hello-ses project and select Manage NuGet Packages.... Search for and install the AWSSDK.SimpleEmail package.

Open Program.cs in the code editor and replace with the code at the end of this step. On line 14, set source to the email address you are using with Amazon SES to send mail.
The code is extremely simple. We create an AmazonSimpleEmailServiceClient with the region and keys from Step 2. We construct a Message representing the email message. We call async SDK method SendMailAsync, passing a SendEmailRequest and receiving back a SendEmaiLResponse. Our sample only targets one recipient but your application could target many.
Program.cs
using Amazon;
using Amazon.SimpleEmail;
using Amazon.SimpleEmail.Model;
using Amazon.SimpleEmail.Internal;
if (args.Length < 3)
{
Console.WriteLine("Usage: dotnet run -- [destination-address] [access-key] [secret-access-key]");
Environment.Exit(0);
}
var region = RegionEndpoint.USWest2;
string source = "your-email-address@somewhere.com";
// Get recipient, access key, and secret key from the command line
string recipient = args[0];
var awsAccessKey = args[1];
var awsSecretKey = args[2];
// Send the email to the recipients via Amazon SES.
using (var client = new AmazonSimpleEmailServiceClient(awsAccessKey, awsSecretKey, region))
{
// Create a send email message request
var dest = new Destination(new List<string> { recipient });
var subject = new Content("Testing Amazon SES through the API");
var textBody = new Content("This is a test message sent by Amazon SES from the AWS SDK for .NET.");
var body = new Body(textBody);
var message = new Message(subject, body);
var request = new SendEmailRequest(source, dest, message);
// Send the email to recipients via Amazon SES
Console.WriteLine($"Sending message to {source}");
var response = await client.SendEmailAsync(request);
Console.WriteLine($"Response - HttpStatusCode: {response.HttpStatusCode}, MessageId: {response.MessageId}");
}
Step 4: Run the Program and Send Some Mail
Our program will send a fixed test message to an email address.
Have the following information ready:
a. A recipient email address to send to. Select one of your Verified identities from Step 1 to use as a recipient email address.
b. Your access key and secret key from Step 2.
Open a command/terminal window, and enter a command line of this form, specifying the recipient email address, your access key, and your secret key. We're doing it this way so you don't have those credentials in your code.
dotnet run -- [recipient-email-address] [access-key] [secret-key]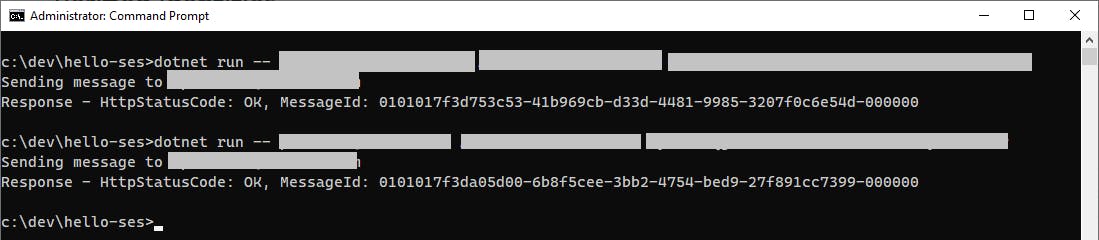
You can watch your message count on the SES dashboard in the AWS console. Refresh the page as needed. The count of messages sent should increase before long. Check the recipient email account to confirm a message was received. The message may not arrive immediately.
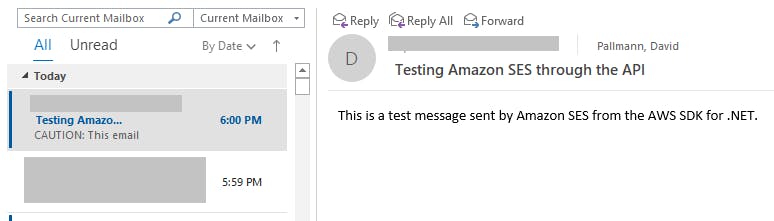
Try other email addresses.
Congratulations! You've sent mail with Amazon Simple Email Service using the AWS SDK for .NET.
Where to Go From Here
In this tutorial you sent email via Amazon Simple Email Service using the AWS SDK for .NET. Amazon Simple Email Service is an easy to use service, and our code tutorial today was very simple. What isn't simple is the general practice of automated sending of email. The public is weary of spam, and that puts the onus on you to protect your reputation.
Take advantage of the sandbox and mail simulator in the AWS console to gain proficiency with SES before you take it live for production use. Invest the time to learn how to use the SES dashboard to monitor bounces, complaints, and delivery problems. Learn about SES facilities for protecting reputation and review the best practices guidance.
Further Reading
AWS Documentation
How email sending works in Amazon SES
Best practices for sending email using Amazon SES
Tutorials
Verified identities in Amazon SES
Videos
Blogs and Code Samples
