Table of contents
- This episode: Amazon Rekognition and Computer Vision. In this Hello, Cloud blog series, we're covering the basics of AWS cloud services for newcomers who are .NET developers. If you love C# but are new to AWS, or to this particular service, this should give you a jumpstart.
- Amazon Rekognition: What is it, and why use It?
- Our Hello, Rekognition Project
- Where to Go From Here
- Further Reading
This episode: Amazon Rekognition and Computer Vision. In this Hello, Cloud blog series, we're covering the basics of AWS cloud services for newcomers who are .NET developers. If you love C# but are new to AWS, or to this particular service, this should give you a jumpstart.
In this post we'll introduce Amazon Rekognition and use it in a "Hello, Cloud" .NET program to recognize images. We'll do this step-by-step, making no assumptions other than familiarity with C# and Visual Studio. We're using Visual Studio 2022 and .NET 6.
Amazon Rekognition: What is it, and why use It?
Amazon Rekognition is a computer vision service that can recognize images and video. As AWS describes it, "Automate your image and video analysis with machine learning." Some use cases for Rekognition include helping locate lost children, preventing human trafficking, and moderating inappropriate content in media uploads.
Rekognition offers several kinds of processing:
- Label detection can detect people, objects, scenes, and activities from images and videos. For example, if your application has something to do with cars, you might care about identifying images of vehicles.
- Content moderation can detect inappropriate, offensive, or unwanted content. For example, you might to exclude user uploads of photos of weapons to your website.
- Face detection can find faces with descriptive attributes such as apparent gender, age range, and whether the person is smiling. Face indexing can add faces to a collection, and face matching can match faces against your collection.
- Recognize celebrities identifies celebrities.
- Face compare lets you compare face images for similarity.
- PPE detection lets you detect personal protective equipment such as face masks, helmets, and gloves.

Although Rekognition is a Machine Learning service, you don't need to train it. You can immediately put the service to work analyzing images and video. As we'll see in our tutorial, the service is easy to experiment with through the AWS console, and easy to program against using the AWS SDK for .NET.
Computer vision and machine learning capabilities can be controversial, and need to be used responsibly. If you've got a potential use case for Amazon Rekognition in mind, be sure your use case is an ethical one, operated with integrity. Consider privacy, the rights of others, and the law. Consider whether automated conclusions need to be paired with human review. Refer to the AWS service terms and Amazon Rekognition best practices for appropriate uses.
Our Hello, Rekognition Project
We’re going to first try out Amazon Rekognition through the AWS console to understand its capabilities. Then, we'll create a .NET 6 console program and use it feed images to Rekognition for a variety of analysis actions, including label detection, image moderation, celebrity face recognition, and face detection. For face detection, we'll also make a copy of the original image with highlighting of the detected faces.

One-time Setup
To experiment with Rekognition and .NET, you will need:
- An AWS account, and an understanding of what is included in the AWS Free Tier.
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2022. If you're using an older version of Visual Studio you won't be able to use .NET 6.
- AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio. Configure the toolkit to access your AWS account and create an IAM user.
Step 1: Set Permissions for the AWS Toolkit User
In order to perform this tutorial, your AWS Toolkit User / default AWS profile needs the necessary permissions for Rekognition operations. In this step, you'll update permissions for your AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio user.
Important: You should always follow the principle of least privilege when it comes to security. This blog series assumes you are working in your own developer account for learning purposes and not working with anything production-related. If you're using an organization-owned AWS account, you should coordinate with your security principal on IAM settings.
- Sign in to the AWS console. Select the region at top right you want to be working in. We're using US West (N. California).
- Navigate to the Identity and Access Management (IAM) area of the AWS Console. You can enter iam in the search box to find it.
- Click Users on the left panel and select the username you use with the AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio (you created this user when you installed and configured the toolkit).
- If not already assigned, add the built-in PowerUserAccess permission. The PowerUserAccess permission provides developers full access to AWS services and resources, but does not allow management of users and groups.
Your AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio user / default AWS profile now have the required permissions for Rekognition operations.
Step 2: Use Amazon Rekognition in the AWS Console
In this step, you'll use Rekognition in the AWS console.
In the AWS console, navigate to Amazon Rekognition . You can enter rekognition in the search bar.
Select Label delection from the left panel. You see a sample document of a skateboarder on a city street, with an analysis of detected labels at right. Try out your own image.
a. Click the Upload button and upload a photo (JPEG or PNG format).
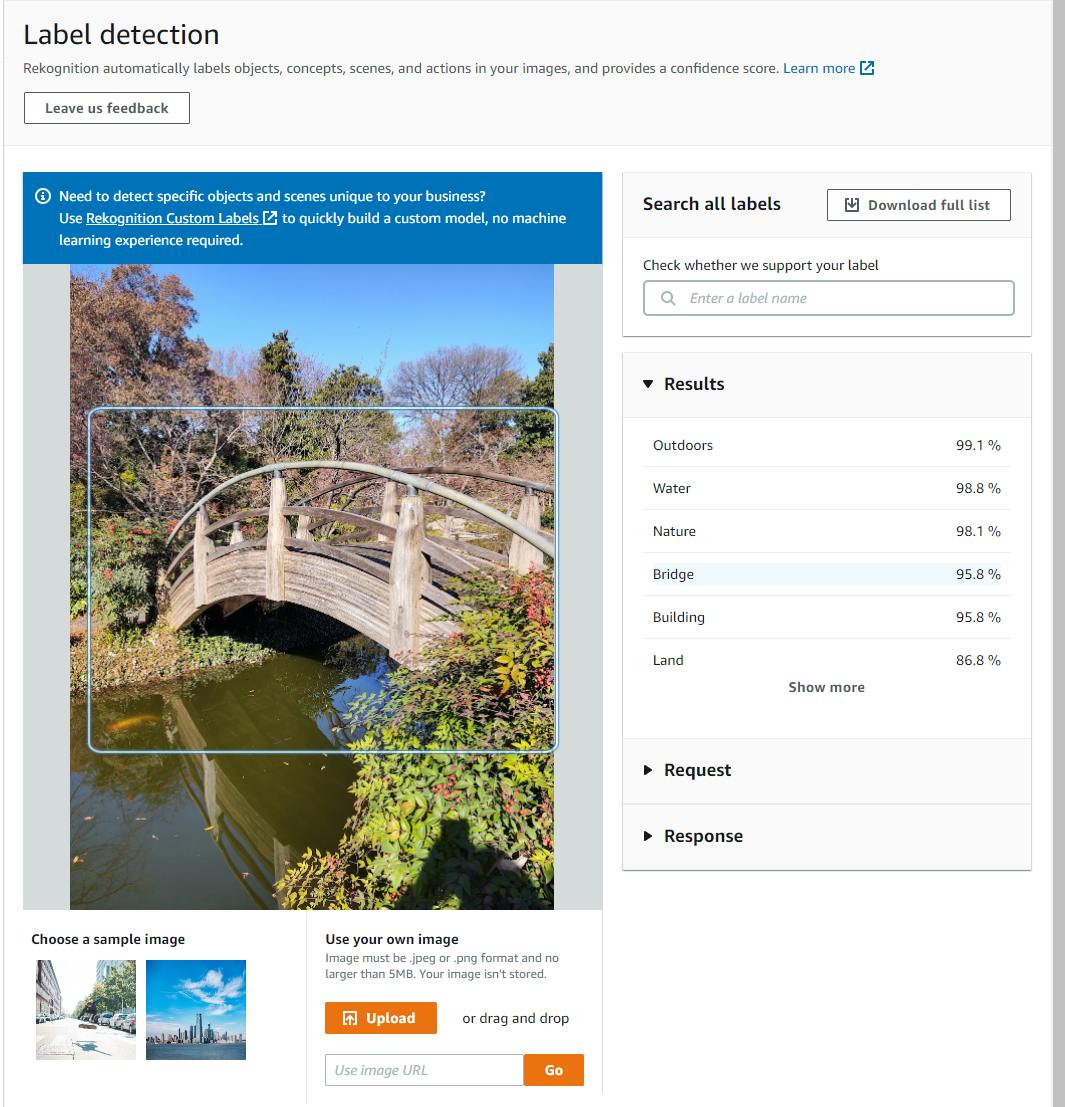
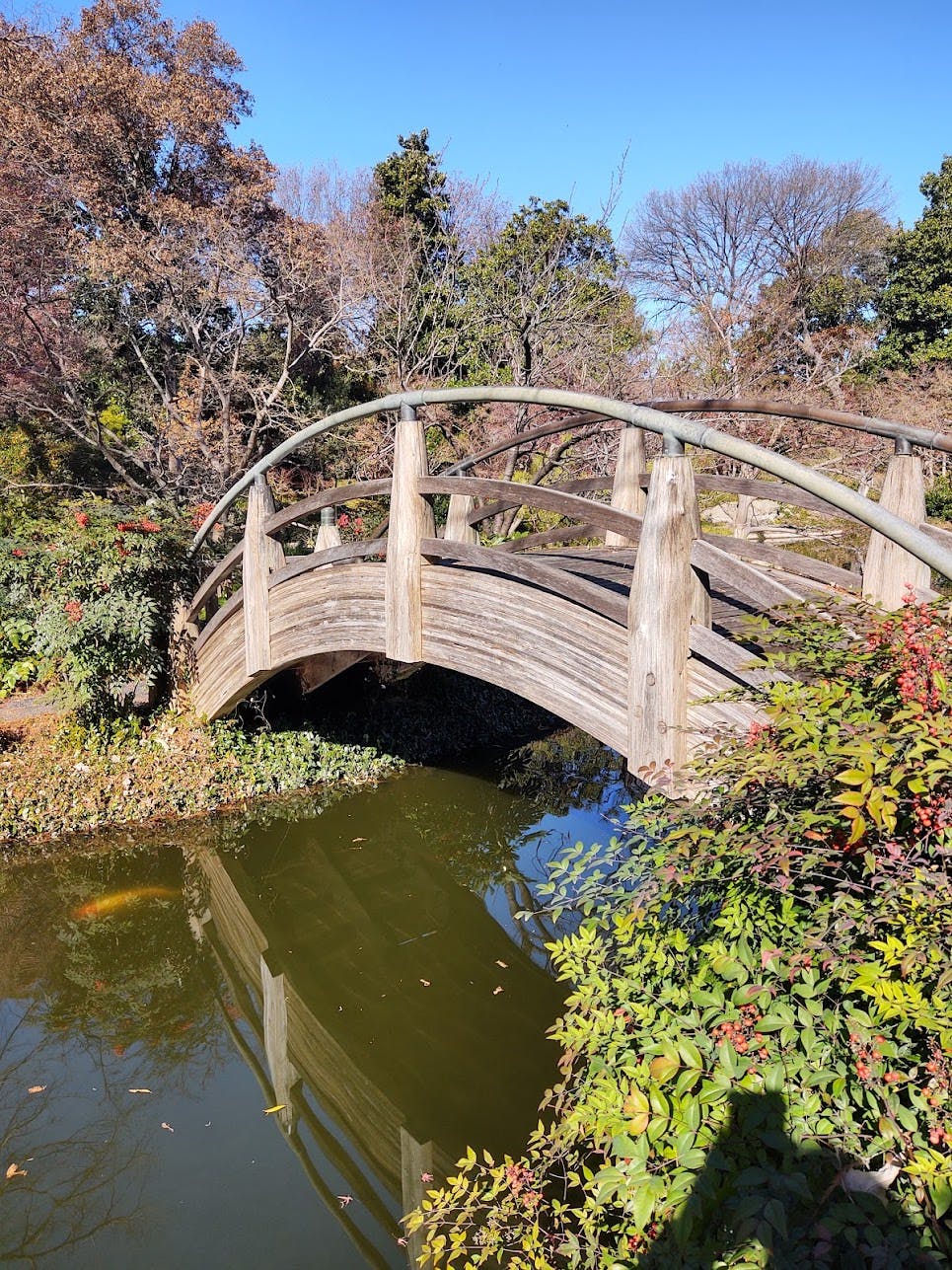
b. Rekognition analyzes the image and displays a series of labels with a confidence rating at right. We tried an image of an outdoors scene with a bridge over water from the Fort Worth Botanic Garden, and Rekognition identified outdoors, water, nature, and bridge with 95%+ confidence.
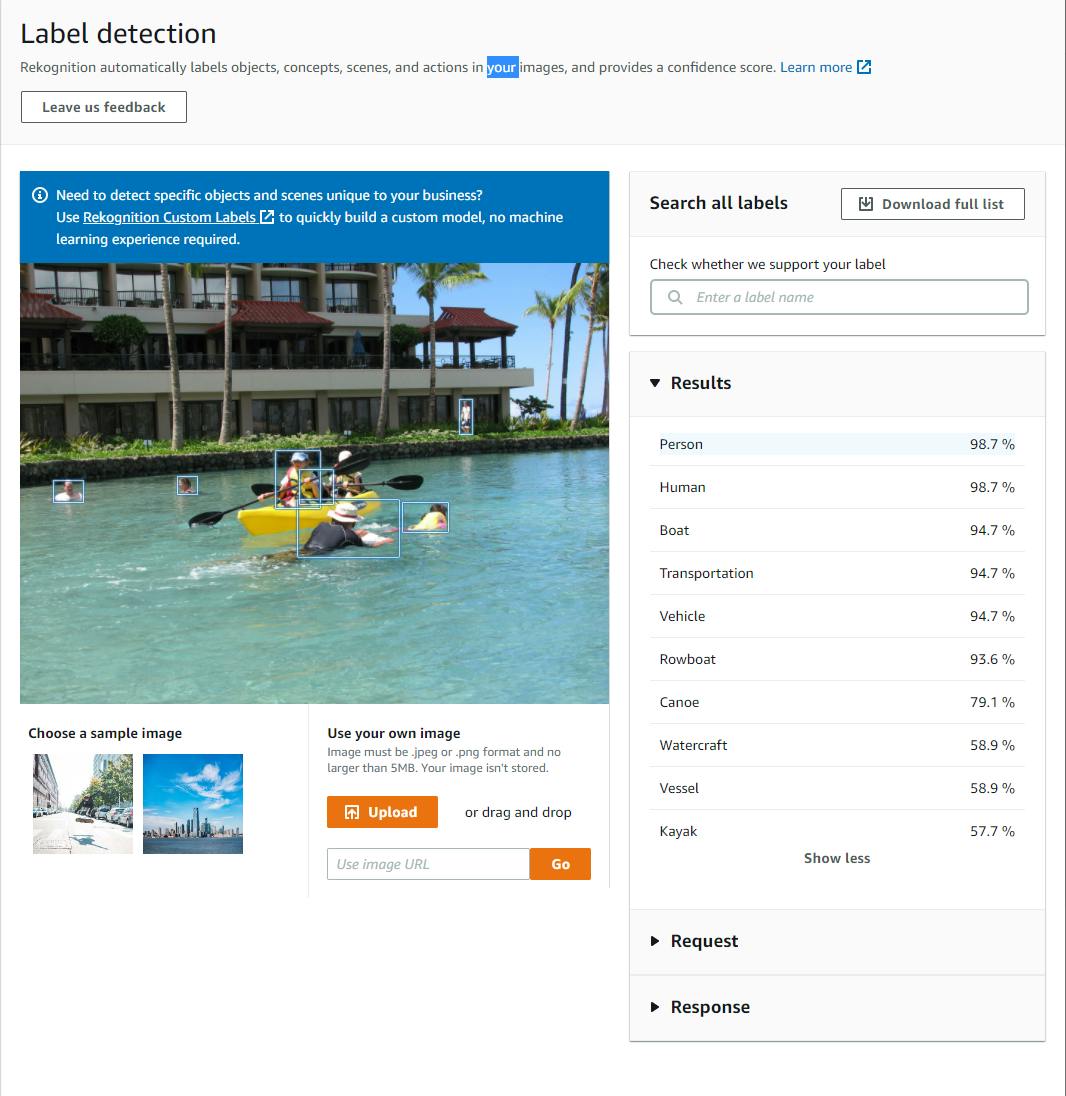
c. Try some additional images. For a vacation photo of my daughters kayaking in Oahu, Rekognition correctly identified people and some kind of watercraft, but was only 57% certain that it was a kayak with this particular photo.
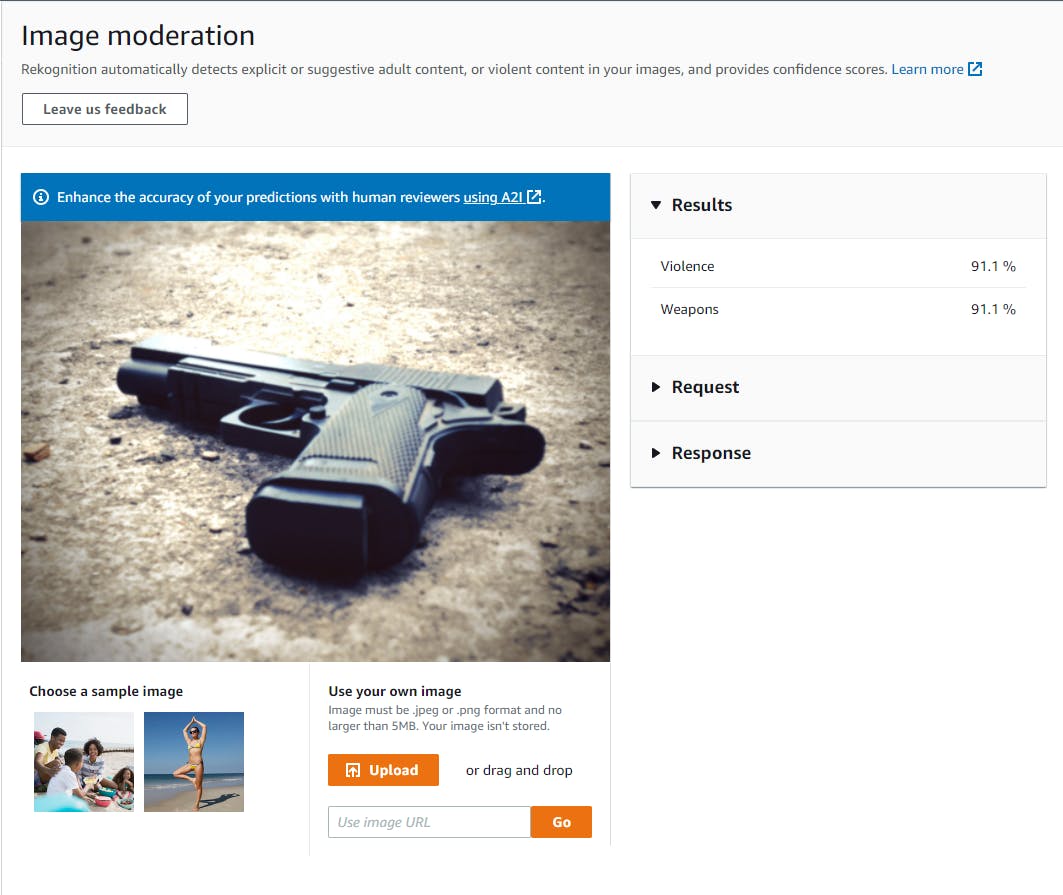
Select image moderation in the left panel. You see an obfuscated photo.
a. Try the two sample photos to see how Rekognition flags potentially problematic content.
b. Click Upload and, without breaking any laws, upload some different kinds of photos to test what Rekognition considers inappropriate. We uploaded a photo of a handgun, which Rekognition flagged as Violence and Weapons with 91.1% confidence.
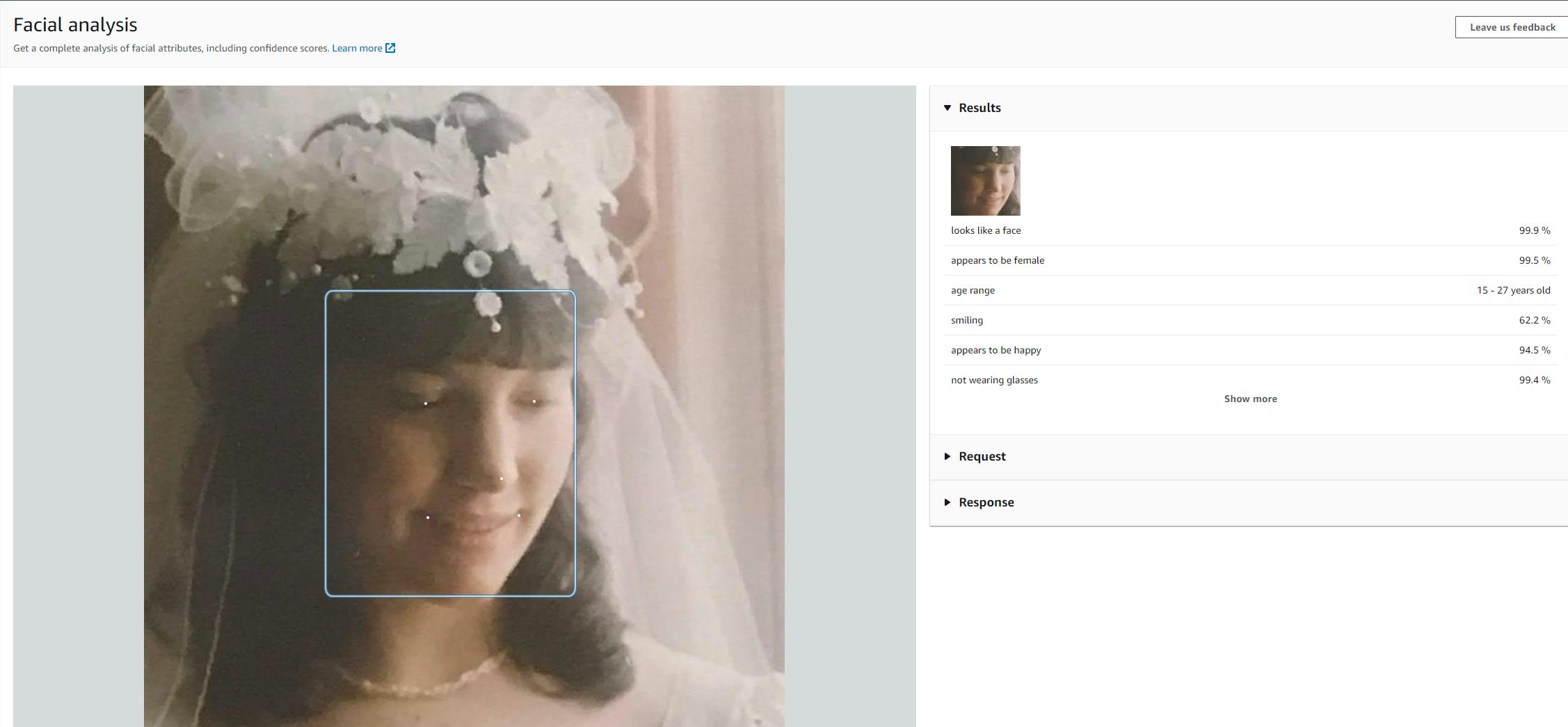
Select Facial analysis in the left panel.
a. Try the two sample images to see how facial detection reports face attributes.
b. Click Upload and upload an image with one or more faces. I uploaded an image of my wife on our wedding day. Rekognition correctly determined a smiling female in her 20's.
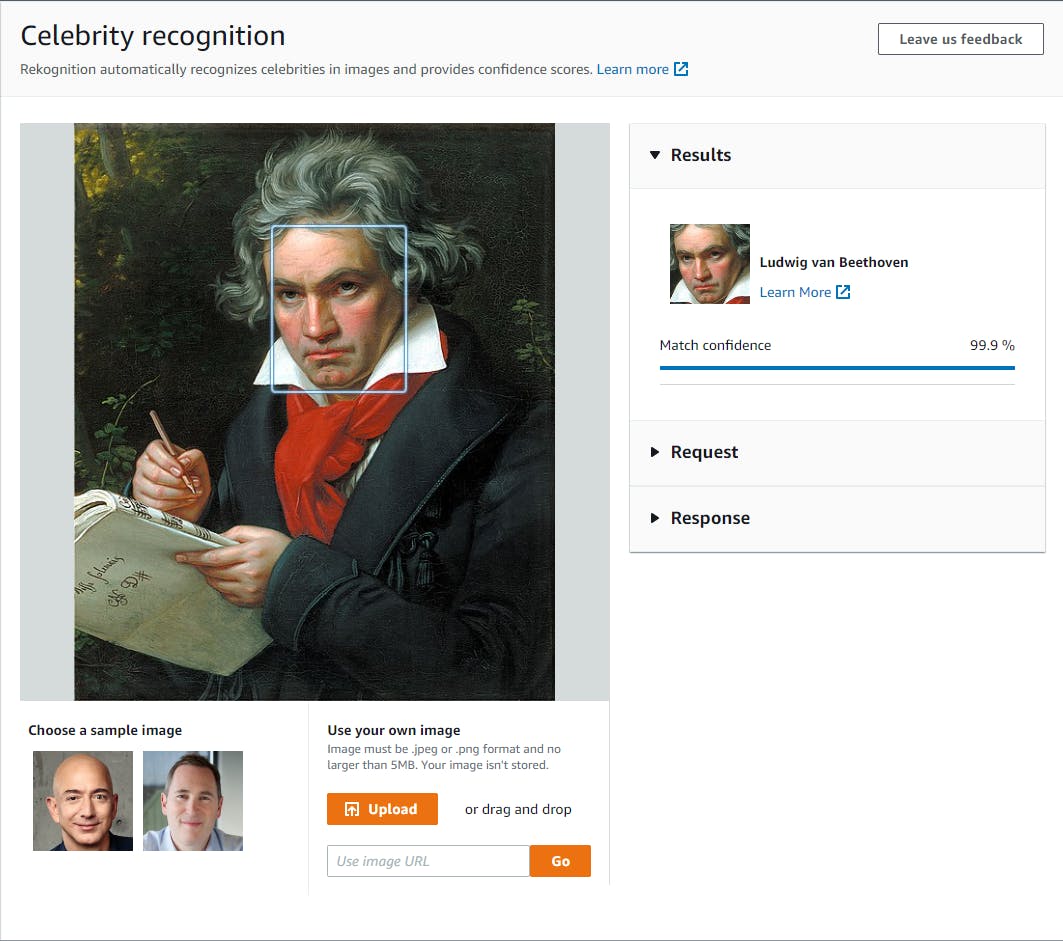
Select celebrity recognition on the left panel.
a. Try each of the two sample images and see that Jeff Bezos and Andy Jassy are recognized with high confidence.
b. Click Upload and test other images. Our image of Ludwig van Beethoven was identified with 99.9% confidence.
Feel free to explore the other options if you wish.
Now that you have a feel for the different capabilities of Amazon Rekognition, it's time to invoke them from .NET code.
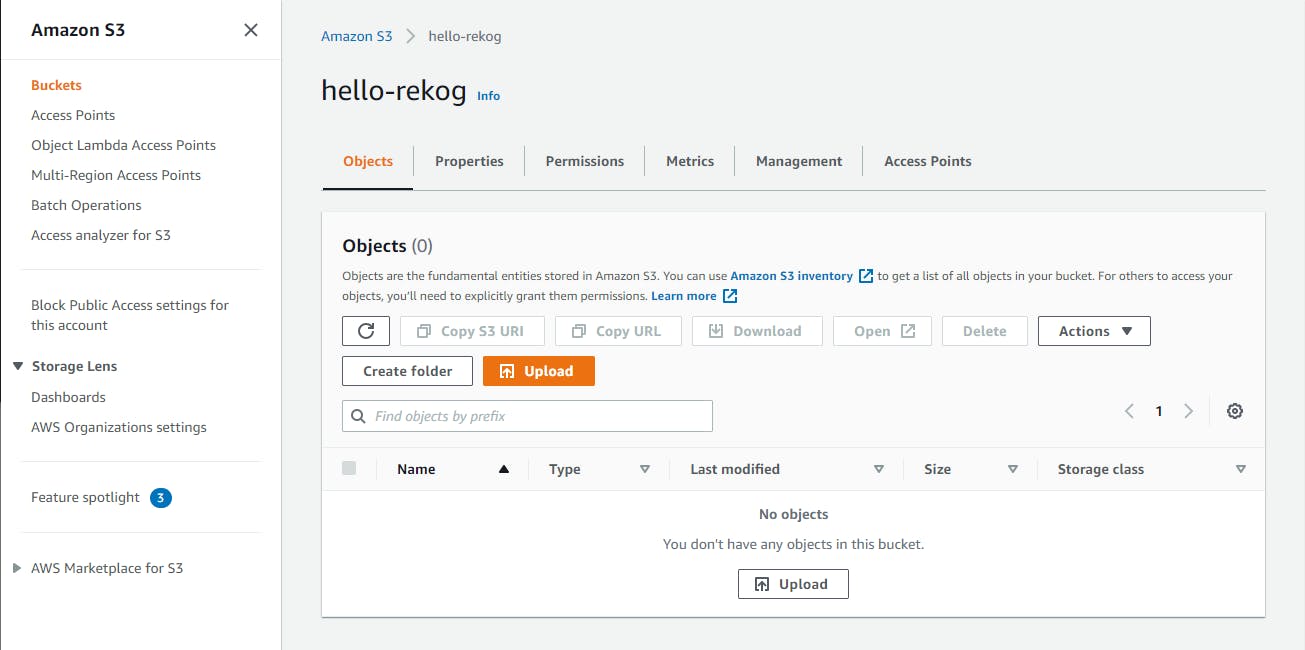
Step 3: Create an S3 Bucket
In this step, you'll create an S3 bucket that our .NET program will upload images to for analysis.
In the AWS console, navigate to Amazon S3. You can type s3 in the search bar.
Select Buckets on the left panel.
Click Create bucket and create a bucket for image uploads. We used the name hello-rekog. If the name you enter is already in use, try a variation of the name.
Step 4: Create a .NET Program
In this step you'll create a .NET console program. The program will accept a local image filename and an action on the command line of labels, moderate, celebrity, or faces.
Open a command/terminal window and CD to a development folder.
Run the dotnet new command below to create a new console program named hello-rekognition.
dotnet new console -n hello-rekognition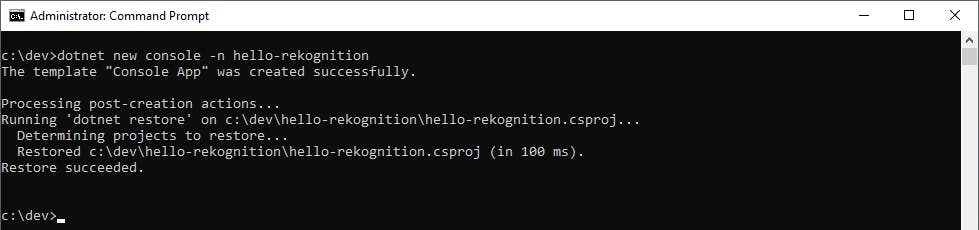
Open the hello-rekognition project in Visual Studio.
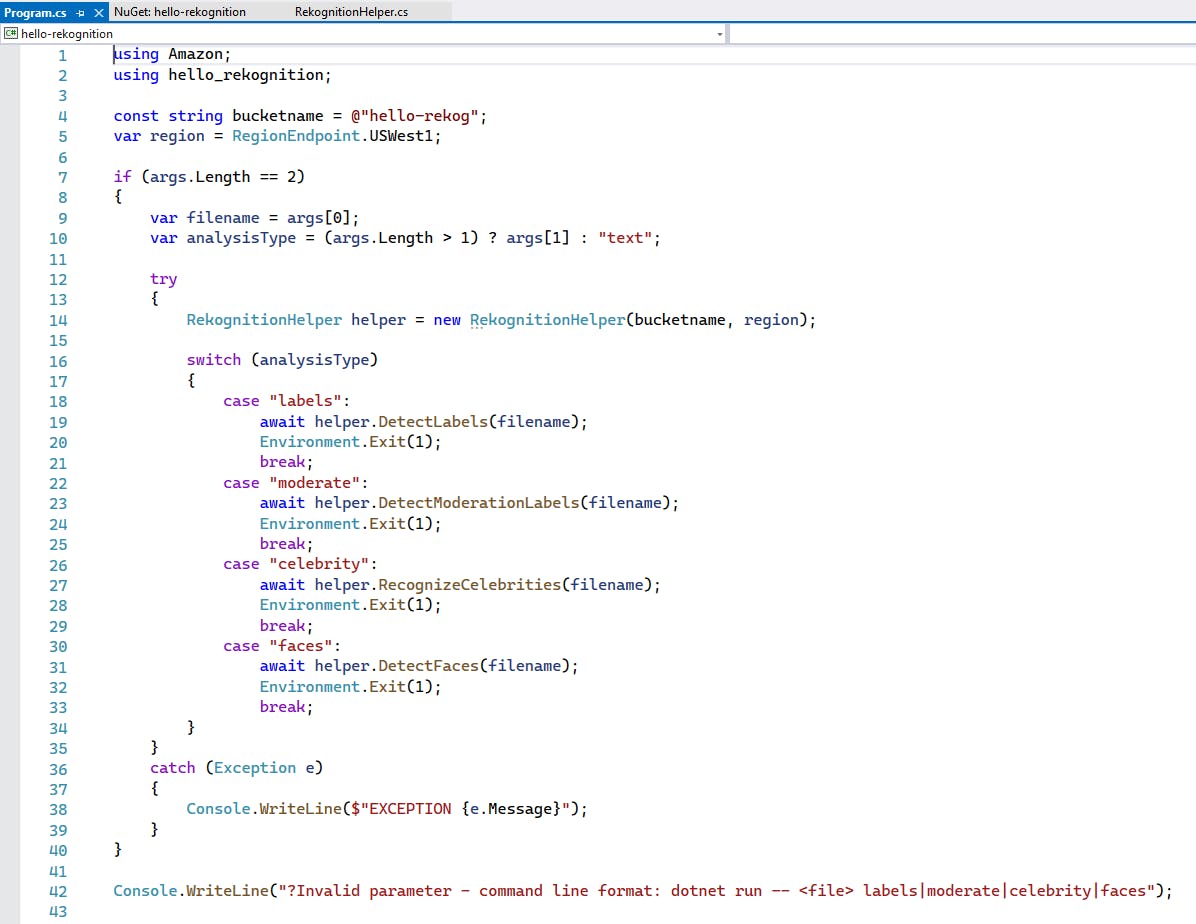
Open Program.cs in the editor and replace with the contents at the end of this step. At the top of the code, replace the bucket name with the name of the bucket you created in Step 3. Replace the region with region where you created the bucket.
The code expects an image filename and an action in command line arguments. In response to actions of "labels", "moderate", "celebrity", or "faces", a method in RekognitionHelper is called to detect labels, moderate an image, recognize celebrities, or detect faces.
In Solution Explorer, add a new class named RekognitionHelper.cs.
Open RekognitionHelper.cs in the editor and replace with the code at the end of this step.
The method for each action uses the same sequence: upload the image to S3, create a request, invoke an asynchronous analysis method, and retrieve data from the response.
Save your changes and build the project.
Program.cs
using Amazon;
using hello_rekognition;
const string bucketname = @"hello-rekog";
var region = RegionEndpoint.USWest1;
if (args.Length == 2)
{
var filename = args[0];
var analysisType = (args.Length > 1) ? args[1] : "text";
try
{
RekognitionHelper helper = new RekognitionHelper(bucketname, region);
switch (analysisType)
{
case "labels":
await helper.DetectLabels(filename);
Environment.Exit(1);
break;
case "moderate":
await helper.DetectModerationLabels(filename);
Environment.Exit(1);
break;
case "celebrity":
await helper.RecognizeCelebrities(filename);
Environment.Exit(1);
break;
case "faces":
await helper.DetectFaces(filename);
Environment.Exit(1);
break;
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine($"EXCEPTION {e.Message}");
}
}
Console.WriteLine("?Invalid parameter - command line format: dotnet run -- <file> labels|moderate|celebrity|faces");
RekognitionHelper.cs
using Amazon;
using Amazon.S3;
using Amazon.S3.Model;
using Amazon.Rekognition;
using Amazon.Rekognition.Model;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
namespace hello_rekognition
{
#pragma warning disable CA1416
public class RekognitionHelper
{
private string _bucketname { get; set; }
private RegionEndpoint _region { get; set; }
private AmazonRekognitionClient _rekognitionClient { get; set; }
private AmazonS3Client _s3Client { get; set; }
public RekognitionHelper(string bucketname, RegionEndpoint region)
{
_bucketname = bucketname;
_region = region;
_rekognitionClient = new AmazonRekognitionClient(_region);
_s3Client = new AmazonS3Client(_region);
}
/// <summary>
/// Detect labels.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="filename"></param>
public async Task DetectLabels(string filename)
{
var image = await UploadFileToBucket(filename);
DetectLabelsRequest detectlabelsRequest = new DetectLabelsRequest()
{
Image = image,
MaxLabels = 10,
MinConfidence = 75F
};
var detectLabelsResponse = await _rekognitionClient.DetectLabelsAsync(detectlabelsRequest);
Console.WriteLine("Detected labels for " + filename);
foreach (var label in detectLabelsResponse.Labels)
Console.WriteLine($"{label.Name}, {label.Confidence}");
await DeleteFileFromBucket(filename);
}
/// <summary>
/// Detect moderation labels.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="filename"></param>
public async Task DetectModerationLabels(string filename)
{
var image = await UploadFileToBucket(filename);
var detectModerationLabelsRequest = new DetectModerationLabelsRequest()
{
Image = image,
MinConfidence = 75F
};
var detectModerationLabelsResponse = await _rekognitionClient.DetectModerationLabelsAsync(detectModerationLabelsRequest);
Console.WriteLine("Detected labels for " + filename);
foreach (var label in detectModerationLabelsResponse.ModerationLabels)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{label.Name}, {label.Confidence}");
}
await DeleteFileFromBucket(filename);
}
/// <summary>
/// Recognize celebrities.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="filename"></param>
public async Task RecognizeCelebrities(string filename)
{
var image = await UploadFileToBucket(filename);
var recognizeCelebritiesRequest = new RecognizeCelebritiesRequest()
{
Image = image
};
var recognizeCelebritiesResponse = await _rekognitionClient.RecognizeCelebritiesAsync(recognizeCelebritiesRequest);
Console.WriteLine("Detected celebrities for " + filename);
foreach (var celebrity in recognizeCelebritiesResponse.CelebrityFaces)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{celebrity.Name}, {celebrity.MatchConfidence}");
}
await DeleteFileFromBucket(filename);
}
/// <summary>
/// Detect faces. Create a copy of original image with faces highlighted.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="filename"></param>
public async Task DetectFaces(string filename)
{
var image = await UploadFileToBucket(filename);
var detectFacesRequest = new DetectFacesRequest
{
Attributes = new List<String>() { "ALL" },
Image = image
};
var detectFacesResponse = await _rekognitionClient.DetectFacesAsync(detectFacesRequest);
Console.WriteLine($"Detected {detectFacesResponse.FaceDetails.Count} face(s) in " + filename);
// create a duplicate image with the faces highlighted
Pen pen = new Pen(Brushes.SkyBlue, 3);
var facesHighlighted = System.Drawing.Image.FromFile(filename);
using (var graphics = Graphics.FromImage(facesHighlighted))
{
foreach(var face in detectFacesResponse.FaceDetails)
{
BoundingBox bb = face.BoundingBox;
Console.WriteLine($" Face found at location ({bb.Top}, {bb.Left}) {bb.Height} x {bb.Width}");
Console.WriteLine($" Gender: {face.Gender.Value}, Age range: {face.AgeRange.Low}-{face.AgeRange.High}, Smiling: {face.Smile.Value}, Eyeglasses: {face.Eyeglasses.Value}, Confidence: {face.Confidence}");
graphics.DrawRectangle(pen, x: facesHighlighted.Width * bb.Left, y: facesHighlighted.Height * bb.Top,
width: facesHighlighted.Width * bb.Width, height: facesHighlighted.Height * bb.Height);
}
}
// Save the image with highlights as a jpeg file
var filenameFacesHighlighted = filename.Replace(Path.GetExtension(filename), "_Faces.jpg");
facesHighlighted.Save(filenameFacesHighlighted, ImageFormat.Jpeg);
Console.WriteLine($"Generated image file {filenameFacesHighlighted} with {detectFacesResponse.FaceDetails.Count} face(s) highlighted.");
await DeleteFileFromBucket(filename);
}
/// <summary>
/// Upload local file to S3 bucket.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="filename"></param>
/// <returns>Amazon Rekognition Image object.</returns>
private async Task<Amazon.Rekognition.Model.Image> UploadFileToBucket(string filename)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Upload {filename} to bucket {_bucketname}");
var putRequest = new PutObjectRequest
{
BucketName = _bucketname,
FilePath = filename,
Key = Path.GetFileName(filename)
};
await _s3Client.PutObjectAsync(putRequest);
return new Amazon.Rekognition.Model.Image
{
S3Object = new Amazon.Rekognition.Model.S3Object
{
Bucket = _bucketname,
Name = putRequest.Key
}
};
}
/// <summary>
/// Delete file from S3 bucket.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="filename"></param>
private async Task DeleteFileFromBucket(string filename)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Delete {filename} from bucket {_bucketname}");
var deleteRequest = new DeleteObjectRequest
{
BucketName = _bucketname,
Key = Path.GetFileName(filename)
};
await _s3Client.DeleteObjectAsync(deleteRequest);
}
}
}
`
Step 5: Run the .NET Program
In this step, you'll run the dotnet program with different images and actions.
Open a command/terminal window and CD to the hello-rekognition project location.
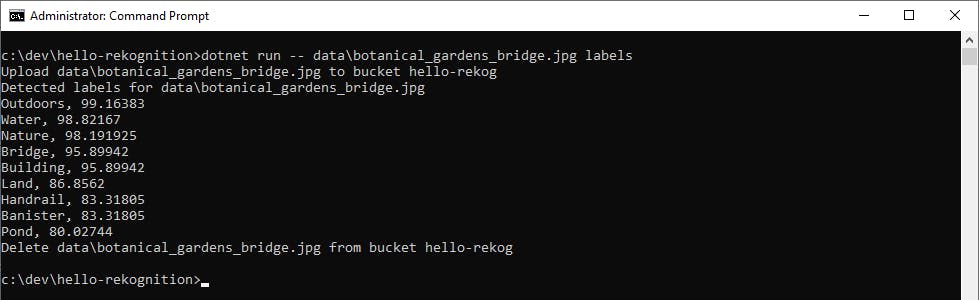
Test Label Detection. Enter dotnet run --
<filename>labels to perform detect labels analysis against an image.In this picture of a bridge at Fort Worth Botanic Garden, Rekognition identifies outdoors, water, nature, bridge, building, land, handrail, banister, and pond.

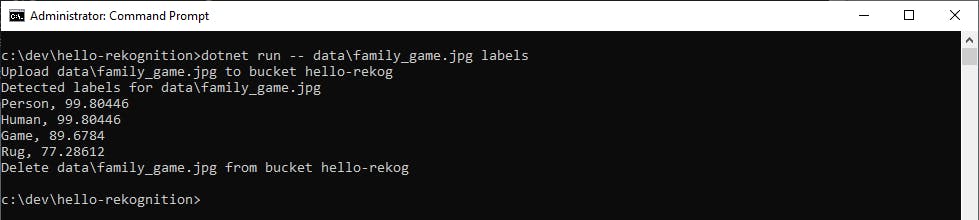
In this picture of family game play, Rekognition identifies person, human, game, and rug. Presumably, "rug" is the quilt hanging over the couch.
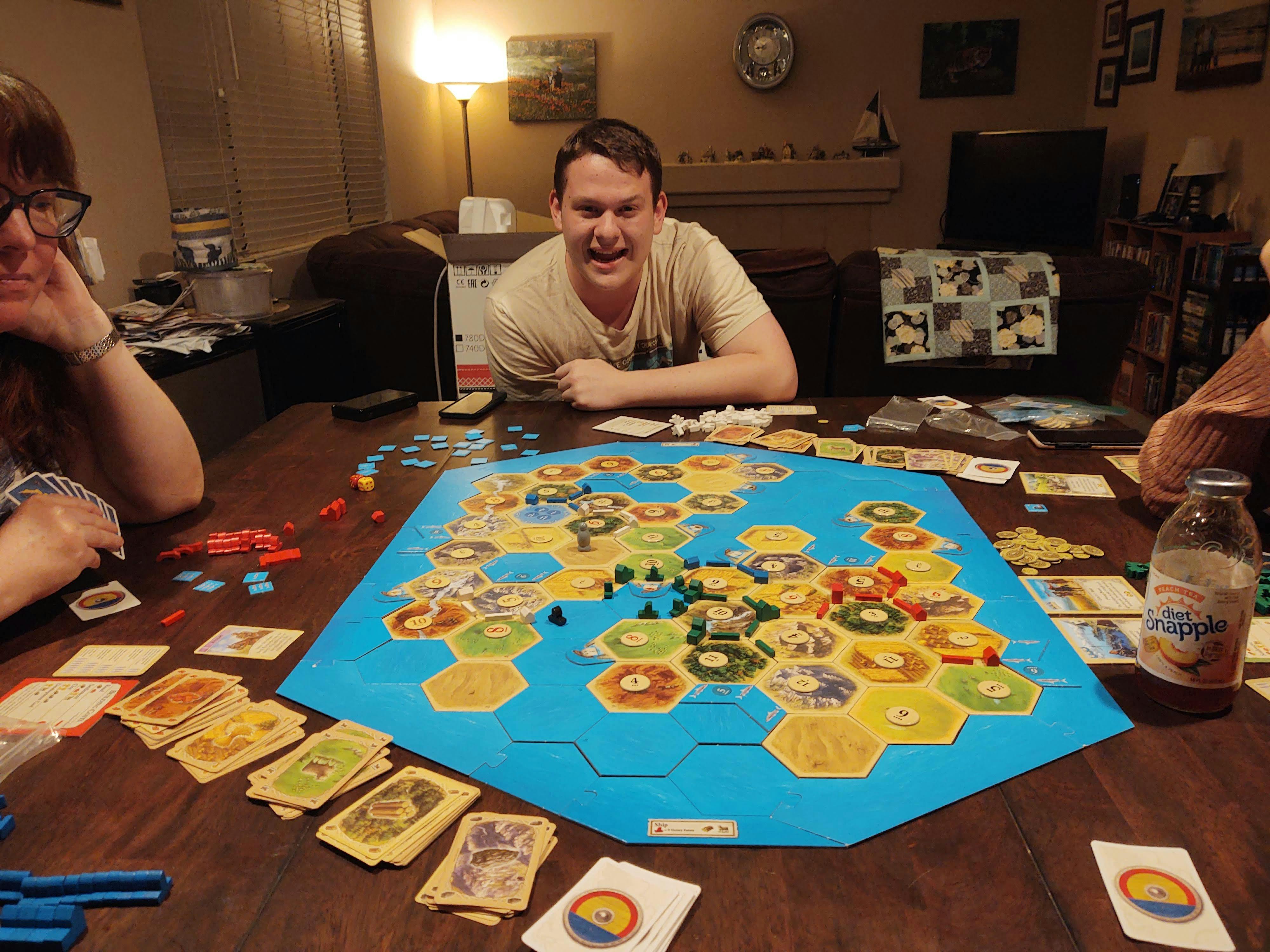

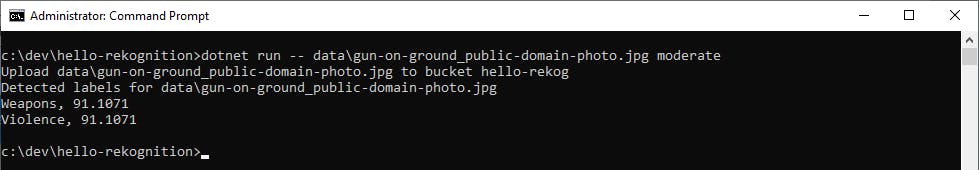
Test Image Moderation. Enter dotnet run --
<filename>moderate to perform image moderation against an image. Rekognition associates this image of a handgun with weapons and violence.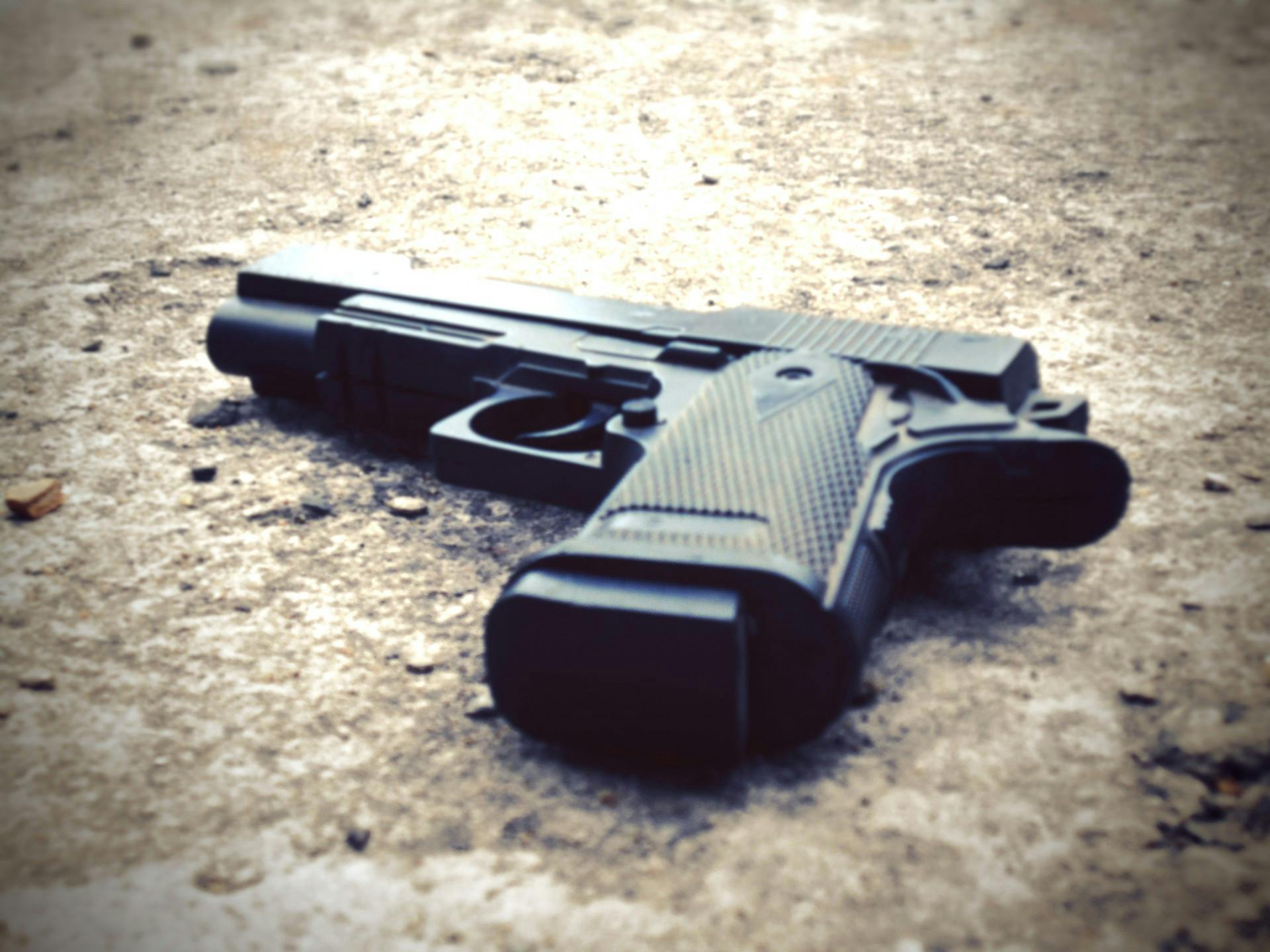
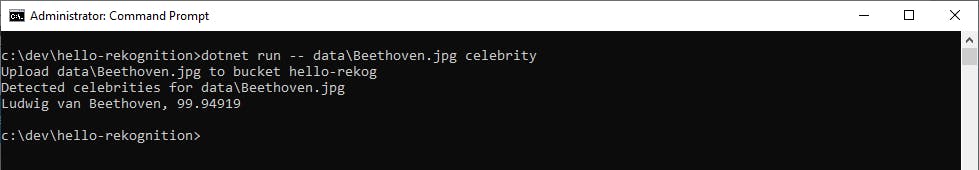
Test Celebrity Face Recognition. Enter dotnet run --
<filename>celebrity to perform celebrity recognition against an image. Although intended for photos, Rekognition property identifies Ludwig van Beethoven from this portrait.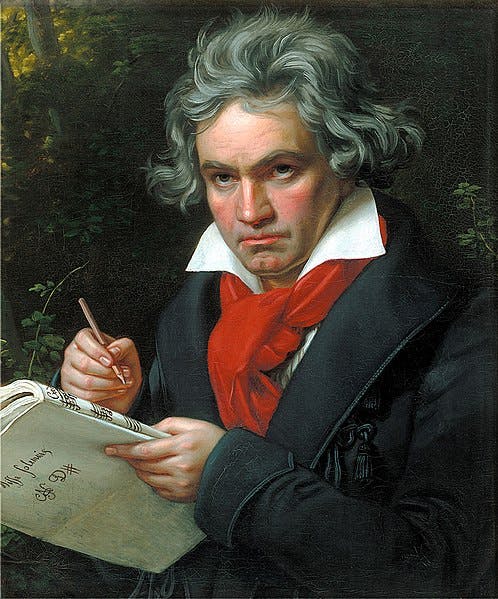
image source: Wikimedia Commons
Test Face Detection. Enter dotnet run --
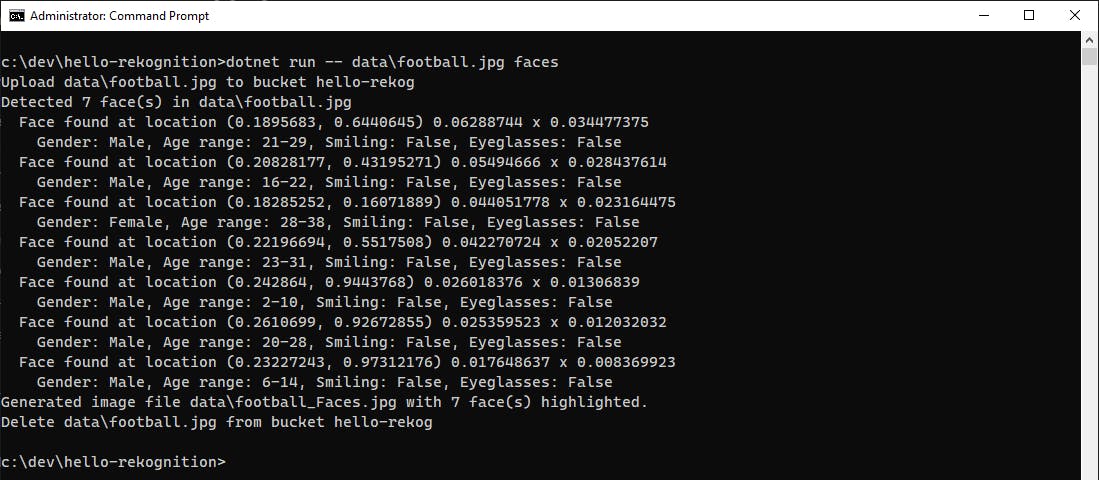
<filename>faces to perform face detection against an image. Try out some different images.Let's see how the program does on an image of my son on a cruise ship at age 6.
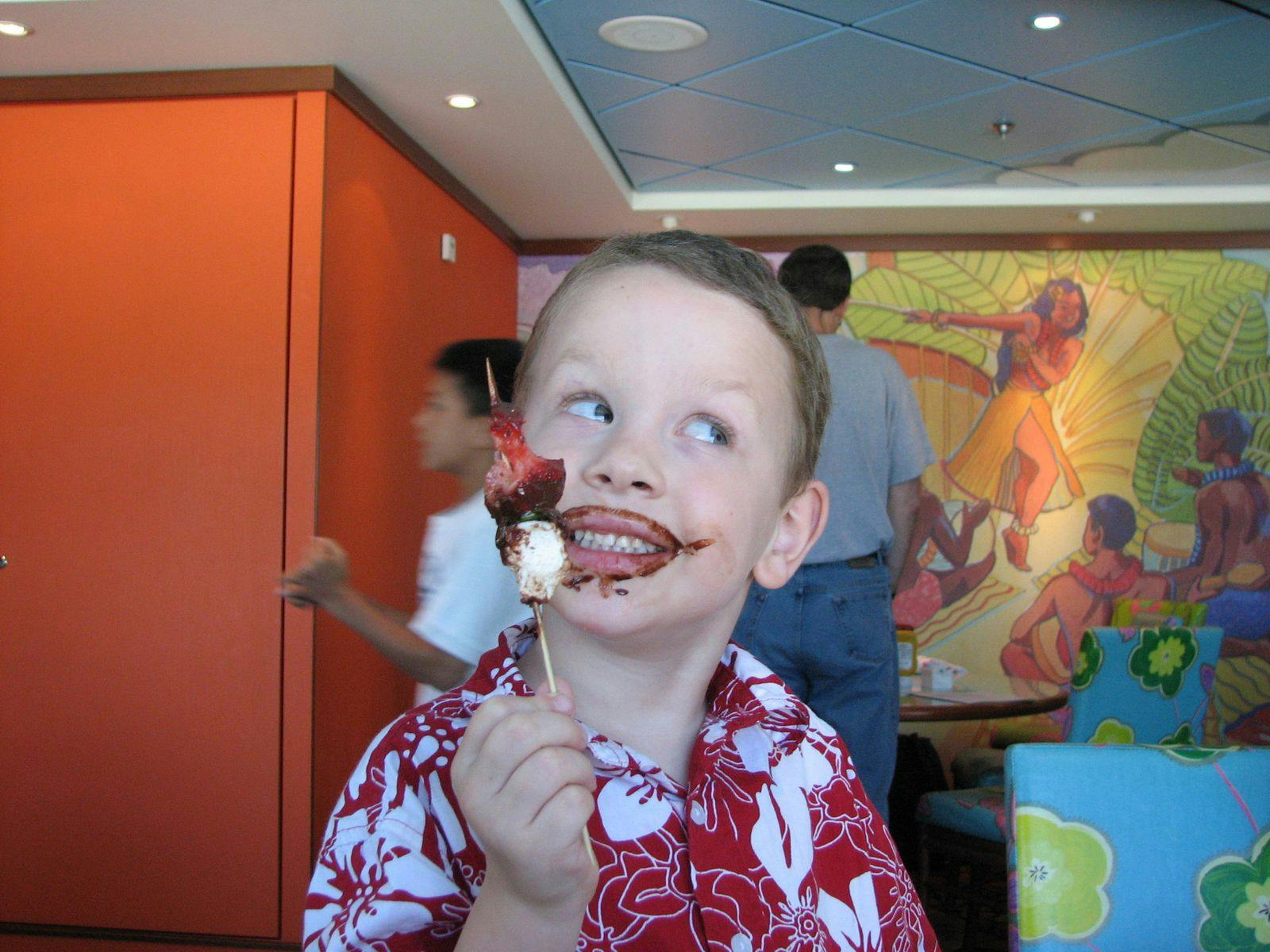

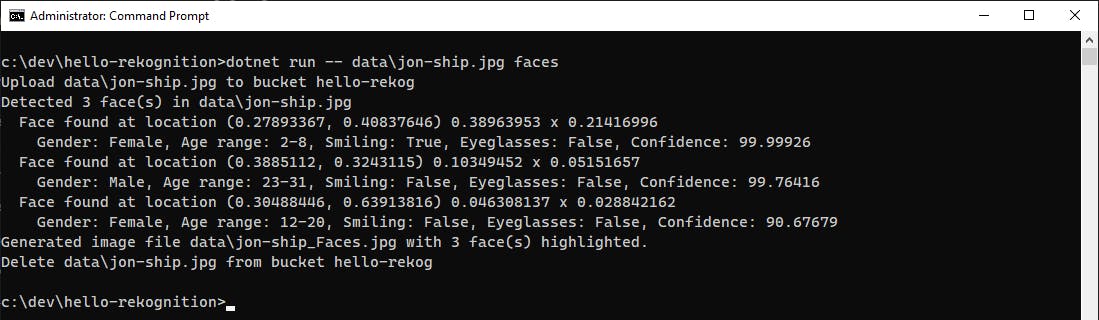
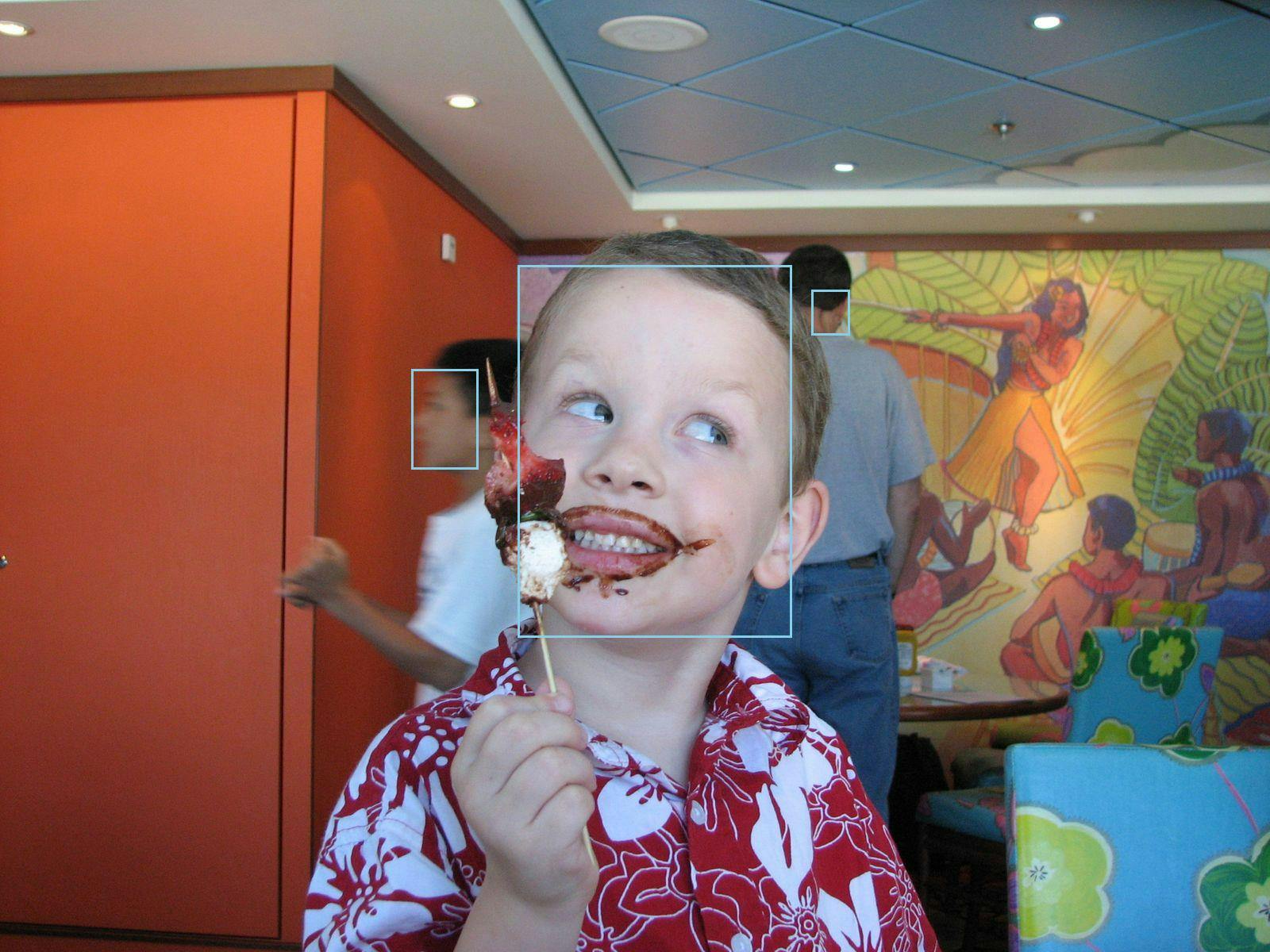
From the output 3 faces were recognized. Looking at the generated image with faces highlighted, we can see that Rekognition finds my son's face in the foreground, as well as a passerby behind him and person facing mostly away in the background. It is not fooled by the faces on the wallpaper. In this case, it reaches some wrong conclusions on gender, which brings up an important point: your applications can get insights from machine learning but should treat them as probabilities, not facts.
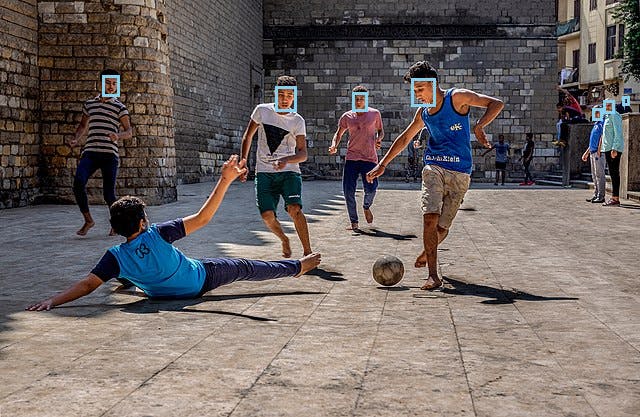
Now let's try an image with multiple faces, this public domain image of boys in Egypt playing football.

image source: Wikimedia Commons
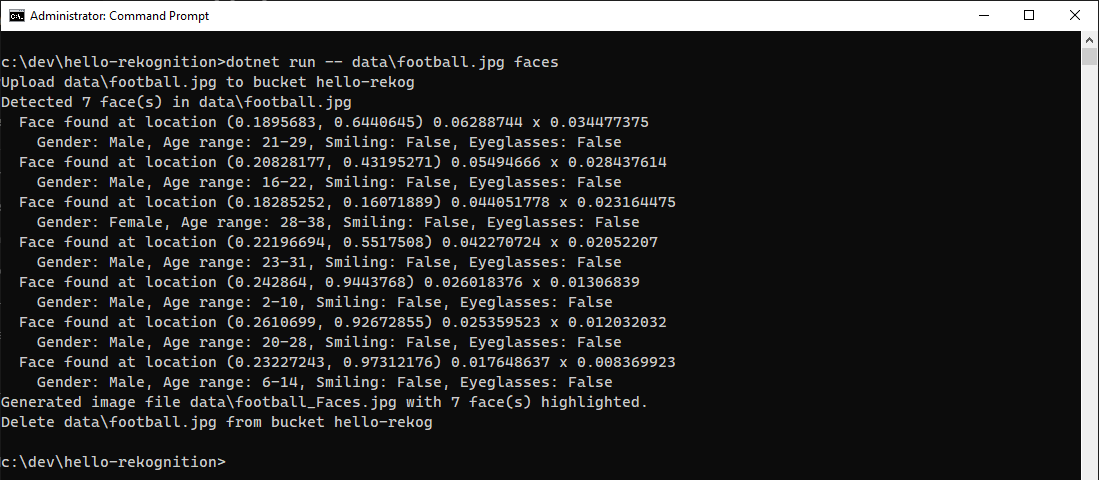
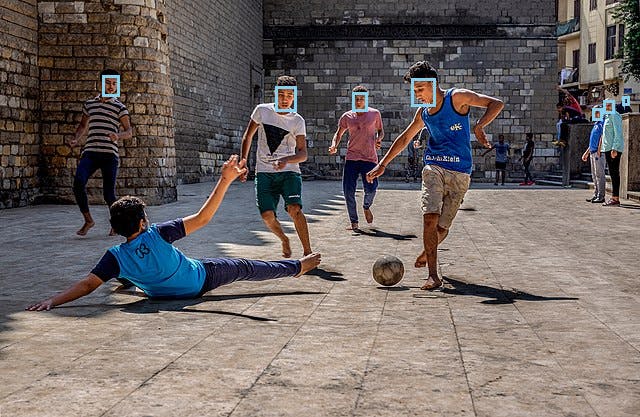
From the output, we see that 7 faces were recognized. Now look at the output image football_faces.jpg that was created. The 7 faces are highlighted in blue bounding boxes.

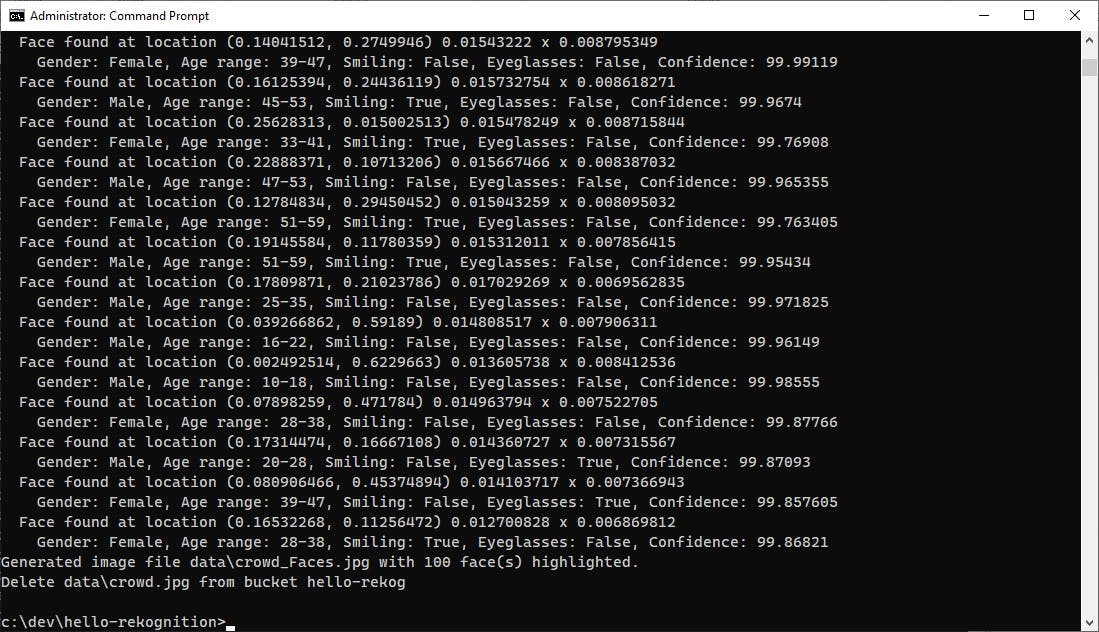
Finally, let's try something more challenging, a picture of a crowd at a NASA space shuttle launch. Rekognition finds 100 faces in this high-resolution photo. image source: Wikimedia Commons
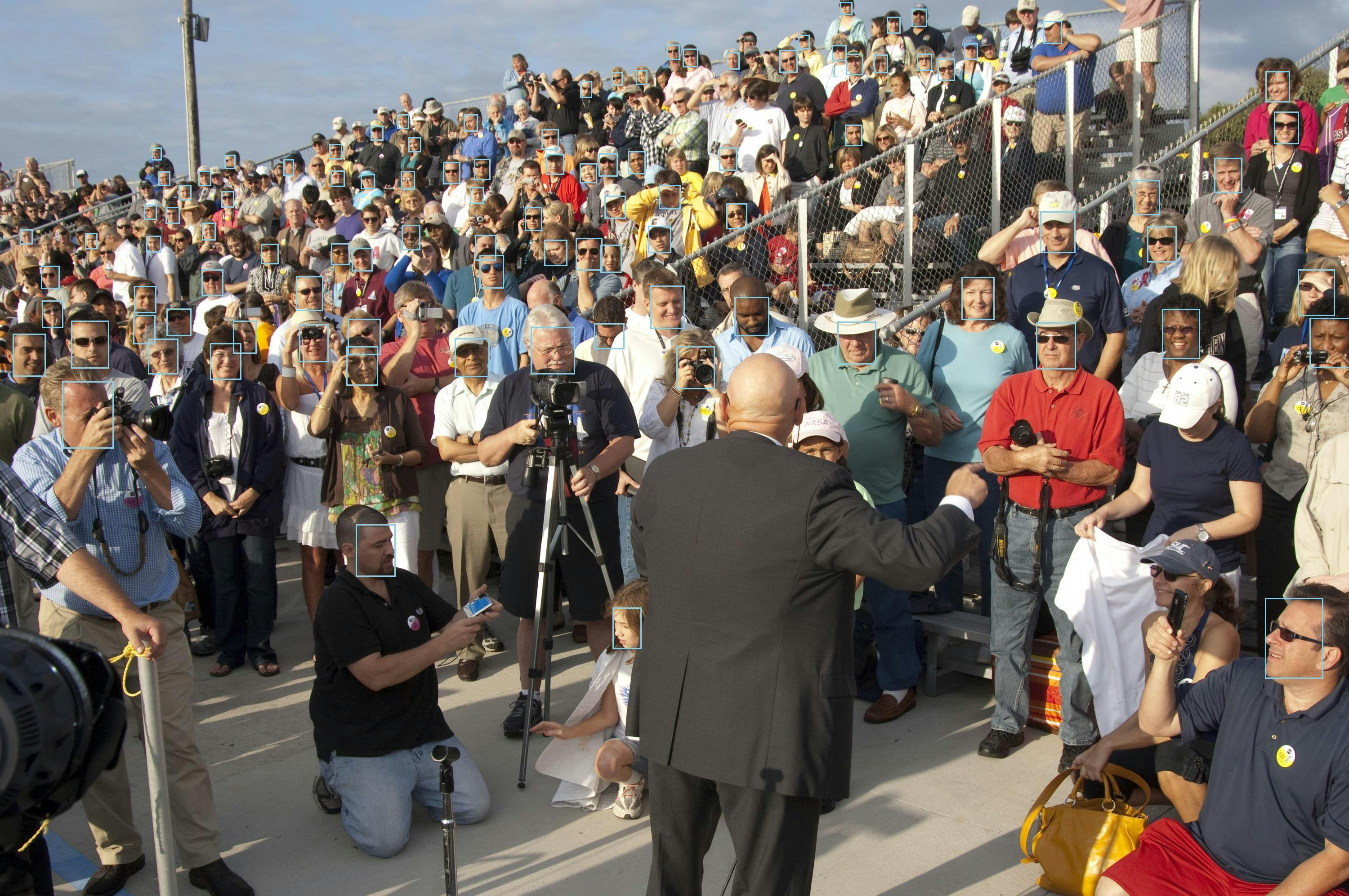


Congratulations! You've worked with computer vision in a number of ways from .NET code using Amazon Rekognition.
Step 6: Understand the Code
Now that we've seen the program run, let's understand the code.
Program.cs simply gets two arguments from the command line, an image filename and an action string, then lets the RekognitionHelper class do all the work. The class is instantiated with the bucket name and region we want to use. A switch statement then calls the appropriate method of RekognitionHelper to do the processing with Rekognition and output results to the console.
In RekognitionHelper, an AmazonRekogitionClient is instantiated in the constructor. All of the action methods follow a similar structure. They upload the specified image to S3 and call a Rekognition method, passing a request object and receiving a response object.
The DetectLabels method calls the SDK's DetectLabelsAsync function and receives in the response a Labels collection with name and confidence fields.

The DetectLabelsModeration method calls DetectLabelsModerationAsync, receiving a ModerateLabels collection of labels flagged for moderation.
The RecognizeCelebrities method calls RecognizeCelebritiesAsync, receiving a CelebrityFaces collection with name and confidence fields.

The RecognizeFaces method starts out similarly to the other action methods, calling RecognizeFaces and receiving a Faces collection in the response. The code goes on to make a copy of the image and uses System.Drawing primitives to highlight the face bounding boxes reported by Rekognition.

Where to Go From Here
Computer vision is an exciting capability that comes with the responsibility of appropriate use. In this tutorial, you got familiar with the different kinds of image analysis that Amazon Rekognition offers. You wrote .NET code to perform four kinds of image analysis using the AWS SDK for .NET, and saw an application of face detection where faces were highlighted in a derived image. Although we worked with images today, you can also analyze video with Amazon Rekognition.
By now, potential uses for Amazon Rekognition are no doubt coming to mind. You could use Amazon Rekognition in a web site, perhaps to screen and moderate media uploads. For example, you might want to disallow food reviews that show peoples' faces, or obfuscate the faces. You could use Amazon Rekognition in AWS Lambda functions that are triggered by S3 image uploads.
Read up on Amazon Rekognition to learn its full set of features and best practices. Experiment with the service to know its mechanics and behaviors well. Use that informed understanding to use Amazon Rekognition with integrity in your applications.
Further Reading
AWS Documentation
Getting started with Amazon Rekognition
Best practices for sensors, input images, and videos
Amazon Rekognition Developer Guide
Recommendations for Facial Comparison Input Images
Tutorial: Creating an Amazon Rekognition Lambda Application
Videos
How Amazon Rekognition helps in the fight against some of the worst types of crime
Using Amazon Translate, Amazon Polly, and Amazon Rekognition with .NET by Thorr Giddings
Using Amazon Rekognition with .NET 5 by Brian Beach
Blogs
